The ExprEvaluator class
and the
Infix Expression Evaluation Demo
Beta 5.0, June 17, 2013, July 28, 2018
The InfixEvalDemo demonstrates the buildFromInfix and evaluate methods in
ExprEvaluator.java.
ExprEvaluator is intended to be an easy use library type class like the classes in the JDK that can be used
in other programs. It can evaluate infix, prefix, and postix expressions. Basically the user supplies variable
values and an expression. One calls the a routine that forms an expression tree from the expression.
The expression tree can then be evaluated as many times as desired. Calculations are done in double
precision. "a", "b", "c", ...., "z" can be used as variables although "t:, "x", and "y" are somewhat preferred.
"+", "-", "*", "/" and "^" can be used along with over 30 different functions.
Using the ExprEvaluator class
The ExprEvaluator class is intended to be easy to use class. InfixEvalDemo just demonstrates
some of its capabilities. It could be used in other Java programs whenever it is desirable to allow the user
to input a prefix, infix or postfix expression that will be evaluated by the program.
The following shows a very simple example of how the ExprEvaluator class can be used. Lines
1 - 7 input values for x, y, and the infix expression to be evaluated. Line 10 forms an expression
tree for the expression. Line 11 shows one of the ways the expression can be evaluated for the
given values.
1 System.out.print("Enter the value for x: ");
2 xVal = scan.nextDouble();
3 System.out.print("Enter the value for y: ");
4 yVal = scan.nextDouble();
5 scan.nextLine(); // read rest of line
6 System.out.print("Enter the expression to be evaluated: ");
7 infix = scan.nextLine();
8 // evaluate expression
9 try {
10 evaluator.buildFromInfix(infix);
11 infixVal = evaluator.evaluate(0, xVal, yVal); // t = 0
12 System.out.println("x =" + xVal + ", y = " + yVal
13 + ", expression = " + infixVal);
14 } catch (Exception e) {
15 System.out.println ("Error: namely: " + e);
16 }
In line 10, one can use buildFromPrefix or buildFromPostfix to process prefix and postfix expressions.
There are 4 different evaluate functions to handle different situation. The buildFrom... functions actually
return the expression tree so more than one expression can be processed.
The demo requires a Java 1.5 or higher add-on to be installed in your browser. If needed, you can down
load a free copy from http://www.java.com/en/
|
Examples using the above InfixEvalDemo
The above image shows the InfixEvalDemo with the "Use variables t, x, y without '='" option selected.
values for t, x, and y were provided and the infix expression was evaluated. Actually the "values" for t, x, and y can
be infix expressions as well. They are evaluated top to bottom. Note: The ap's output actually includes a visual
of the expression tree but it hidden in the image to reduce the space needed for the image.
|
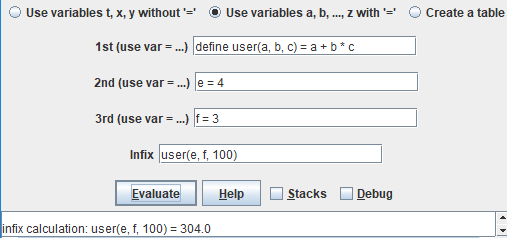
With Use variables a, b, ..., z with "=" selected, a user function is defined and values provided for
e and f.
Then the function is evaluated using e, f, and 100
as the parameter values.
|
|
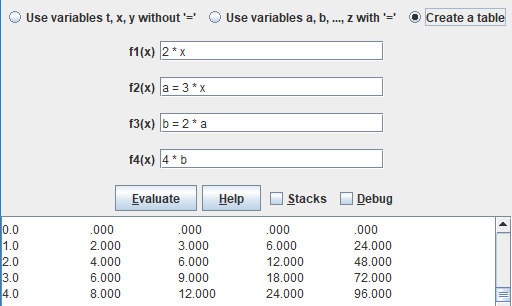
The Create a table option creates a table with x automatically incremented from 0 to 5. A function
tree is created for each of the 4 functions which are evaluated in order. As shown in the example,
b in
f3(x) uses the value of a calculated by f2(x) and f4(x)
uses that value in its calculation. The columns could
be labeled "x", "f1(x)", "f2(x)", "f3(x)", and "f4(x)".
|
In the "Use variables t, x, y without '='" mode, the demo uses 4 instances of ExprEvaluator - one
for each of t, x, y, and infix. That means that it is possible to use infix expressions for t, x, and y. This allows several interesting uses. Here are some examples:
| t | x | y | Infix | Comment |
| t + 2 | 2 * t | 2 * x | 2 * y |
Adds 2 to the old value of t, sets x to twice the value of t, sets y to twice
the value of x and then calculates twice the value of y. For example,
if the old value of t was 0, the new t would be 2, x becomes 4, y becomes 8
and the value of the infix expression is 16. |
| | | | sqrt(3^2 + 4^2) |
Evaluates the hypotenuse of a right triangle with sides 3 and 4. |
| 3 | 4 | sqrt(x^2 + y^2) |
Evaluates the hypotenuse of a right triangle with sides x and y. |
| | 3 | (4/3)*x | sqrt(x^2 + y^2) |
Evaluates the hypotenuse of a right triangle with sides x and (4/3)x. |
| | 0 | | (x-4)/(x-5) |
Evaluates (x-4)/(x-5) when x = 0. |
| | x+.1 | | (x-4)/(x-5) |
Evaluates (x-4)/(x-5) with x increasing by .1 each time the expressions are evaluated. |
| 30 | cos(toRadians(t)) | sin(toRadians(t)) | |
Calculates the x and y coordinates of the point on the unit circle at the angle of 30 degrees. |
| t + 10 | cos(toRadians(t)) | sin(toRadians(t)) | sin(2*toRadians(t))^2 |
Calculates the x, y, and z coordinates of the point above the unit circle with angle t increasing by 10 degrees
each time the expressions are evaluated. The z value is [sin(2t)]2 |
In the "Use variables a, b, ... z with '='" mode, the demo uses only 1 instances of ExprEvaluator .
Here are a few examples:
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | Infix | Comment |
| | a = 3 | b = 4 | sqrt(a^2 + b^2) | Evaluates the hypotenuse of
a right triangle with sides a and b.
|
| a = 3 | b = 4 | c = 2 | |
Evaluate a polynomial with 3 constant parameters.
This is a two part example. First assign values to a, b, and c.
Then follow up with assigning values to x and y. Can be
repeated with new values of x and y. |
| | x = 3 | y = 4 | a*x^2 + b*x*y + c*y^2 |
Comments about the ExprEvaluator class
In the case of illegal calculations such as 1/0, log(-1), or sqrt(-1), the result will typically be infinity, -infinity, or NaN
(Not a Number).
ExprEvaluator originally was developed for a Data Structures class that demonstrated stacks and binary
trees. It only operated with numbers and the binary operators +, -, *, /. It could build binary expression trees
from both infix and postfix expressions. This version expands it by allowing the ^ operator, functions, unary
operators + and -, variables a, b, c, ..., z, as well as constants PI and E.
ExprEvaluator can be used in nearly any program where it is desirable to allow the user to input an
prefix, infix or postfix expression that needs to be evaluated. The class was designed to be very easy to use as
illustrated by TrivialExample1.java. Suppose that the infix expression
is contained in the String expr and the values of t, x, and y are stored in tVal, xVal, and yVal. All that is
needed to evaluate the expression into a variable exprVal are these lines of code:
ExprEvaluator evaluator = new ExprEvaluator();
...
try {
evaluator.buildFromInfix(infix);
exprVal = evaluator.evaluate(tVal, xVal, yVal);
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println ("Error: namely: " + e);
}
When it is desired to evaluate several different functions the following code style could be
used:
ExprEvaluator evaluator = new ExprEvaluator();
ExprTree [ ] tree = new ExprTree[3];
String [ ] expr = new String[3];
double x;
double [ ] val = new double[3];
expr[0] = ...
expr[1] = ...
expr[2] = ...
...
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
tree[i] = evaluator.buildFromInfix(expr[i]);
for (x = ...; x < ...; ...)
setX(x);
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
val[i] = evaluator.evaluate(tree[i]);
...
}
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println ("Error: namely: " + e);
}
If the expression is prefix or postfix instead of infix, the only change would be to be to replace
"buildFromInfix" by "buildFromPrefix" or "buildFromPostfix".
For additional information, please look at the Javadoc files
for ExprEvaluator.
Downloading the files
Down load the beta copy as a .zip file. Included files:
The class requires Java 1.5 or higher
Comments and questions
Please send any comments, corrections, questions, or suggestions to James Brink
brinkje@plu.edu.
Copyright James Brink, 2008, 2013. Permission to use the package for non-commercial use is hereby granted.
Revised 5/17/13


